The broad immunomodulatory properties of human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) has allowed for wide application in regenerative medicine as well as immune/inflammatory diseases including severe pulmonary injury and inflammation such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) associated with bacterial and viral infections. In light of the novel COVID-19 pandemic, MSC therapy (MSCT) has emerged as a possible candidate despite the lack of preclinical data of MSCs for COVID-19. Dr. B. Linju Yen from the Institute of Cellular and System Medicine has been invited by Stem Cells Translational Medicine to review the mechanistic evidence for clinical use of MSCs in pulmonary immune/inflammatory disorders, and survey the ongoing clinical trials—including for COVID-19—of MSCT for these diseases, with some perspectives and comment on MSCT for COVID-19.
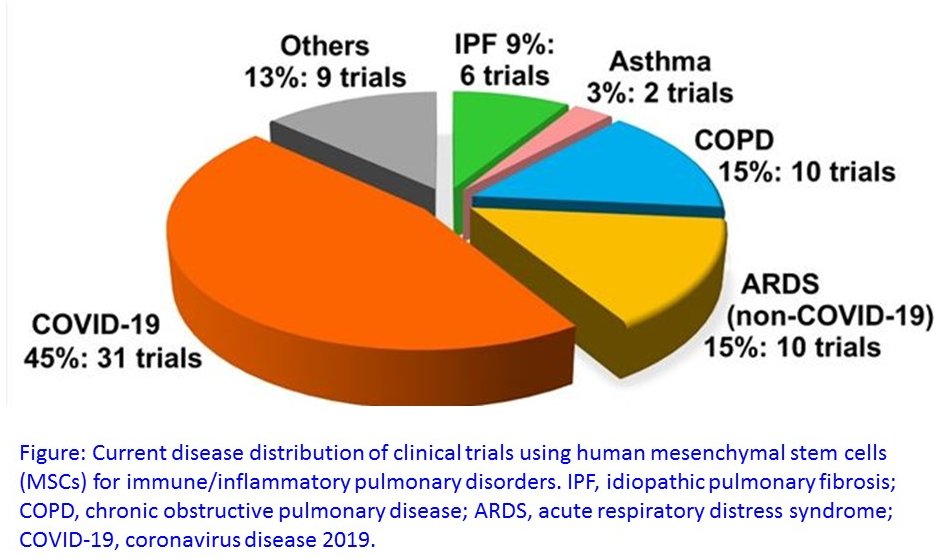
Based on Dr. Yen and collaborators’ review, MSCT preclinical data specifically on immune/inflammatory disorders of the lungs were among the earliest to be reported in 2003, with the first clinical use of MSCT for graft-vs-host disease reported in 2004. Since these first reports, preclinical data showing beneficial effects of MSC immunomodulation have accumulated substantially, and as a consequence, over a third of MSCT clinical trials now target immune/inflammatory diseases. There is much preclinical evidence for MSCT in noninfectious—including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis—as well as infectious bacterial immune/inflammatory lung disorders, with data generally demonstrating therapeutic effects; however, for infectious viral pulmonary conditions, the preclinical evidence is more scarce with some inconsistent outcomes. The prospect of MSCT for COVID-19, therefore, must be tempered with strict evaluation of patient inclusion/exclusion criteria as well as stringent ethical consideration to foremost protect patient safety.
Citation: Yen, B. LJ; Yen, ML; Wang, LT; Liu, KJ; Sytwu, HK. Current status of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for immune/inflammatory lung disorders: Gleaning insights for possible use in COVID-19. Stem Cells Translational Medicine 2020. DOI: 10.1002/sctm.20-0186
