A team led by Dr. Tze-Sing Huang from the National Institute of Cancer Research, in collaboration with Taipei Veterans General Hospital, reported extracellular HSP90α (eHSP90α) can be potentially taken as a target to suppress pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) pathogenesis besides myeloid cells.
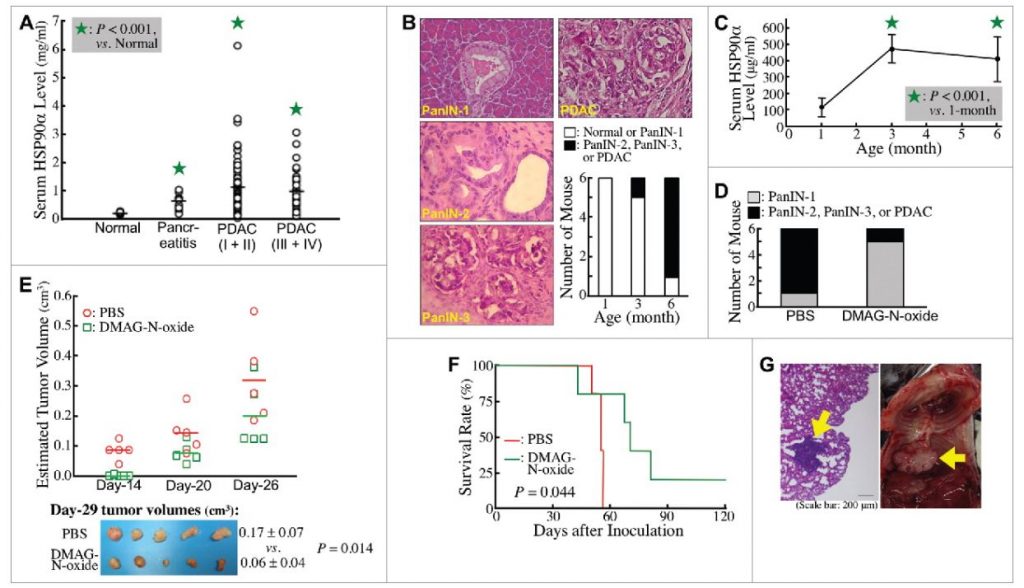
The team detected a significant elevation of serum HSP90α levels in pancreatitis patients and even more in PDAC patients. However, no significant difference in the serum HSP90α levels between patients with early-stage and late-stage PDAC was detected. LSL-KrasG12D/Pdx1-Cre transgenic mice were used as a studying model to study whether elevation of serum HSP90α levels occurred early during PDAC development. Elevated serum HSP90α levels were detected before PDAC formation and an eHSP90α inhibitor effectively prevented PDAC development. Both serum HSP90α level and pancreatic lesion were suppressed when the mice were administered a CD11b-antagonizing antibody, suggesting that CD11b+-myeloid cells were associated with eHSP90α levels and pancreatic carcinogenesis.
Consistently, in CD11b-DTR-EGFP transgenic mouse model with CD11b+-myeloid cells depletion, serum HSP90α levels were suppressed and Panc-02 cell grafts failed to develop tumors. Macrophages and granulocytes are two common tissue-infiltrating CD11b+-myeloid cells. Duplex in situ hybridization assays suggested that macrophages were predominant HSP90α-expressing CD11b+-myeloid cells during PDAC development. Immunohistochemical and immunohistofluorescent staining results revealed that HSP90α-expressing cells included not only macrophages but also pancreatic ductal epithelial (PDE) cells. Cell culture studies also indicated that eHSP90α could be produced by macrophages and macrophage-stimulated PDE cells. Macrophages not only secreted significant amount of HSP90α, but also secreted interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 to induce a JAK2−STAT3 signaling axis in PDE cells, stimulating them to express and secrete HSP90α. eHSP90α further promoted cellular epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration, and invasion in PDE cells. These findings have recently been published in OncoImmunology (2018 April; 7(5): e1424612).
