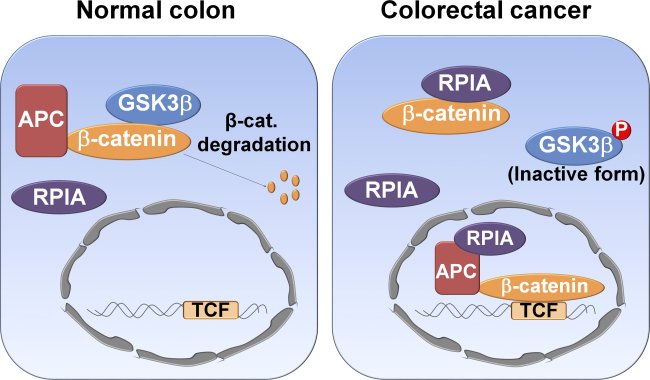
Model of the RPIA mechanism for induction of β-catenin signaling in colorectal cancers
The Institute of Molecular and Genomic Medicine has demonstrated a novel function of ribose-5-phosphate isomerase A (RPIA) in colorectal cancer formation. The team, led by Dr. Chiou-Hwa Yuh, in collaboration with Dr. Horng-Dar Wang, Institute of Biotechnology, National Tsing-Hua University recently published their findings in PLoS Biology (2018 Jan 16;16(1):Article number e2003714).
RPIA is a key enzyme in pentose phosphate pathway (PPP). The dysregulation of PPP is known to promote tumorigenesis. However, the molecular mechanism of RPIA-mediated colorectal cancer formation is unknown. Dr. Yuh’s team showed that RPIA is significantly elevated in colorectal cancer tissues. RPIA increased cell proliferation and oncogenicity via increaseing β-catenin protein level, and activating β-catenin downstream target genes. RPIA enters the nucleus, also forms a complex with adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) and β-catenin. Further investigation suggested that overexpression of RPIA stabilized β-catenin by preventing its phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and subsequent degradation. In addition, the C-terminus of RPIA (amino acids 290 to 311), a nonenzymatic domain was not previously characterized, is necessary for RPIA-mediated tumorigenesis. In addition, the team also observed that gut expression of RPIA increases the expression of β-catenin and its target genes and induces tumorigenesis in transgenic zebrafish. These findings suggest that RPIA can enter the nucleus and associate with APC/β-catenin, which suggest precise treatment of human colorectal cancer by targeting its nonenzymatic domain.
Chou, YT;Jiang, JK;Yang, MH;Lu, JW;Lin, HK;Wang, HD;Yuh, CH. Identification of a noncanonical function for ribose-5-phosphate isomerase A promotes colorectal cancer formation by stabilizing and activating β-catenin via a novel C-terminal domain. PLoS Biology. 2018 Jan 16;16(1):Article number e2003714.
